Mutual funds vs ETFs – which one is right for you?
Written: Editor | July 12, 2023

Advantages and Disadvantages of Mutual Funds
Benefits of Investing in Mutual Funds
Mutual funds offer several benefits to investors, making them a popular choice for many. Some key advantages include:
-
Diversification: By pooling together funds from multiple investors, mutual funds offer a diversified portfolio of investments. This helps to mitigate risk and reduce the impact of individual stock or bond performance on the overall portfolio.
-
Professional Management: An experienced team of fund managers handle the selection and management of investments in a mutual fund. This expertise can be valuable for investors who may not have the time, knowledge, or resources to effectively manage their own portfolios.
-
Liquidity: Mutual funds are generally highly liquid, meaning investors can buy or sell their shares at the current net asset value (NAV) at any time. This provides flexibility and access to funds when needed.
-
Accessibility: Mutual funds are available to a wide range of investors, including those with small amounts to invest. This makes them a convenient option for individuals looking to start investing without a large initial capital investment.
Drawbacks of Mutual Funds
Despite their advantages, mutual funds also have some potential drawbacks to consider:
-
Fees: Mutual funds come with various fees, including management fees, administrative fees, and sales charges. These fees can reduce overall returns and eat into the investor's profits.
-
Lack of Control: When investing in a mutual fund, investors relinquish control over the individual securities held in the portfolio. This means that they rely on the fund manager's decisions and may not have direct influence over investment choices.
-
Tax Considerations: Mutual funds can be subject to capital gains taxes, especially if the fund manager buys and sells securities within the portfolio. This can result in tax implications for investors, potentially reducing their after-tax returns.
Key Considerations when Choosing Mutual Funds
When selecting mutual funds, investors should consider the following factors:
-
Investment Objective: Determine whether the fund aligns with your investment goals, such as growth, income, or preservation of capital.
-
Risk Tolerance: Assess your risk tolerance to find a fund that matches your comfort level with market volatility.
-
Performance History: Evaluate the fund's past performance, looking for consistent returns and how it compares to relevant benchmarks.
-
Fees and Expenses: Understand the fees associated with the fund and consider their impact on potential returns.
By carefully considering these factors, investors can choose mutual funds that suit their investment needs and preferences.

Advantages and Disadvantages of ETFs
Benefits of Investing in ETFs
Exchange-Traded Funds, or ETFs, have gained popularity among investors for various reasons:
-
Diversification: ETFs offer a wide range of investment options that allow investors to access different asset classes, sectors, and regions. This diversification can help spread out investment risk.
-
Liquidity: ETFs trade on stock exchanges, providing investors with the ability to buy or sell shares throughout the trading day at market prices. This liquidity allows for flexibility and ease of trading.
-
Lower Costs: ETFs generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds. They passively track specific indexes, which means they require less active management and have lower costs associated with research and analysis.
-
Transparency: ETFs provide transparency as they disclose their holdings on a daily basis. Investors can easily track the underlying assets and monitor their performance.
Drawbacks of ETFs
While ETFs have many advantages, there are also some potential drawbacks:
-
Trading Costs: Frequent buying and selling of ETF shares can result in transaction costs, including brokerage fees and bid-ask spreads. These costs can eat into investment returns, particularly for active traders.
-
Limited Control: ETFs are passively managed and simply track an index. This means investors have limited control over the portfolio composition and cannot actively adjust holdings according to their preferences.
-
Price Volatility: ETF prices can be subject to market volatility and may deviate from their net asset value (NAV). During times of heightened market uncertainty, ETF prices may experience greater fluctuations.
Key Considerations when Choosing ETFs
When selecting ETFs for investment, it is important to consider the following factors:
-
Expense Ratio: Compare the expense ratio of different ETFs to find those with lower costs. Lower expense ratios can contribute to higher overall investment returns.
-
Tracking Error: Evaluate the tracking error of an ETF to ensure that it closely follows its underlying index. Lower tracking error indicates better performance alignment.
-
Liquidity: Assess the trading volume and liquidity of an ETF to ensure there is sufficient market depth for buying or selling shares without significant price impact.
-
Asset Class and Strategy: Consider the specific asset class, sector, or investment strategy the ETF focuses on. Make sure it aligns with your investment objectives and risk tolerance.
By carefully weighing the advantages, disadvantages, and key considerations, investors can make informed decisions when choosing ETFs that align with their investment goals.
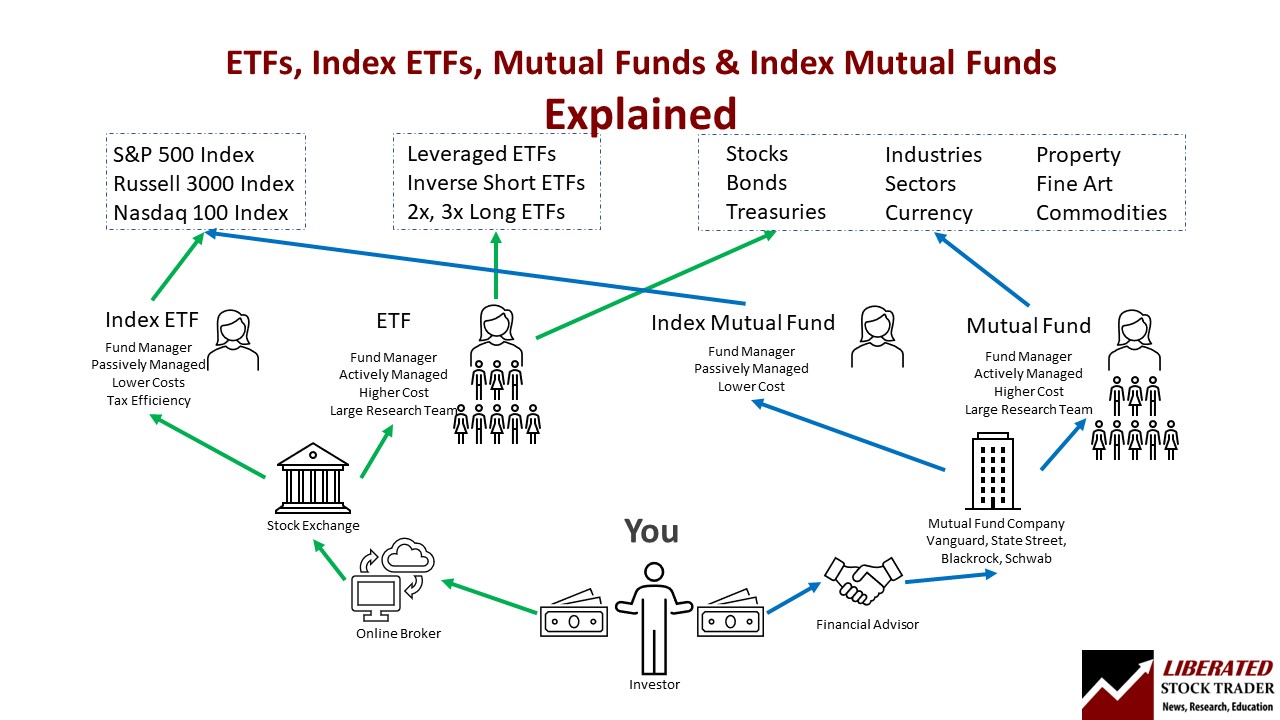
Mutual Funds vs. ETFs: Performance and Returns
Understanding Performance Metrics for Mutual Funds
When evaluating the performance of mutual funds, investors rely on several metrics. These include the fund's net asset value (NAV), which represents the fund's per-share value, and the total return, which incorporates both capital gains and dividends. Additionally, investors assess a fund's expense ratio, which represents the percentage of assets used to cover management fees and other expenses.
Analyzing Performance and Returns of ETFs
Exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are designed to track the performance of specific indexes. As a result, the metrics used to evaluate mutual funds may not be as relevant. Instead, investors typically focus on the tracking error, which represents the deviation of an ETF's performance from its target index.
To understand an ETF's performance, investors also consider the bid-ask spread, which reflects the difference between the highest price that buyers are willing to pay and the lowest price that sellers are willing to accept. Furthermore, investors analyze the liquidity of the ETF, examining its trading volume and average daily volume.
Comparing Mutual Funds and ETFs in Terms of Performance
Both mutual funds and ETFs offer the opportunity for returns, but their performance can differ due to their distinct structures.
Mutual funds are actively managed, with portfolio managers making investment decisions to achieve the fund's investment objectives. This active management can result in higher fees for investors but also offers the potential for outperforming the market.
On the other hand, ETFs passively track specific indexes and are not actively managed. Therefore, they generally have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds. However, their performance is tied closely to the performance of the underlying index.
In conclusion, the choice between mutual funds and ETFs depends on an investor's individual preferences, risk tolerance, and investment goals. Understanding the performance metrics for each investment vehicle can help investors make informed decisions about their portfolios.

Diversification and Investment Strategy
Diversification Benefits of Mutual Funds
Mutual funds offer investors the advantage of diversification. By pooling the funds of multiple investors, a mutual fund can invest in a wide range of securities such as stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments. This diversification helps spread the risk and reduces the impact of any individual investment's performance on the overall portfolio. It allows investors to access a diversified investment portfolio without having to purchase individual securities.
Diversification Benefits of ETFs
ETFs, or exchange-traded funds, also offer diversification benefits. Like mutual funds, ETFs hold a basket of securities, providing exposure to various asset classes or sectors. The key difference is that ETFs trade on stock exchanges, allowing investors to buy and sell shares throughout the trading day. The ability to trade ETFs like individual stocks provides flexibility and liquidity.
Choosing the Right Investment Strategy: Mutual Funds or ETFs?
When deciding between mutual funds and ETFs, investors should consider their investment goals, risk tolerance, and investment preferences.
Mutual funds are suitable for investors looking for a long-term investment vehicle managed by professional fund managers. They are a good option for those seeking diversification and potentially higher returns over time. However, they often come with higher expense ratios and may have sales charges or redemption fees.
On the other hand, ETFs are a suitable choice for investors who value flexibility and liquidity. ETFs can be traded throughout the day, and they usually have lower expense ratios compared to mutual funds. They are particularly attractive to investors who prefer a more hands-on approach and want to actively manage their investments.
In conclusion, both mutual funds and ETFs offer diversification benefits, but the choice depends on individual investment preferences. Understanding your investment goals and risk tolerance will help you make an informed decision between the two investment strategies.
Remember to consult with a financial advisor or do thorough research before making any investment decisions.

Cost and Fees
Management Fees of Mutual Funds
When it comes to investing, one of the key considerations is the cost and fees associated with the investment vehicle. Mutual funds typically charge management fees, which cover the cost of running the fund and are usually a percentage of the amount invested. These fees can vary widely among mutual funds, depending on factors such as the fund's size, investment strategy, and management team. It is important to carefully review and compare the management fees of different mutual funds before making an investment decision.
Fees Associated with ETFs
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) also charge fees, although they typically have lower management fees compared to mutual funds. This is because ETFs are passively managed and aim to replicate the performance of a specific index, rather than actively selecting investments. The fees associated with ETFs include expense ratios, which cover the costs of managing the fund, as well as brokerage commissions when buying or selling ETF shares. It is crucial to consider these fees when evaluating the cost of investing in ETFs.
Comparing Costs and Fees of Mutual Funds and ETFs
When comparing the costs and fees of mutual funds and ETFs, it is important to consider your investment goals and preferences. While mutual funds generally have higher management fees, they offer professional portfolio management and can be actively managed to potentially outperform the market. On the other hand, ETFs tend to have lower fees and may be more suitable for investors who prefer a passive investment approach.
It is worth noting that the costs and fees of both mutual funds and ETFs can impact your overall investment returns. Therefore, it is crucial to carefully evaluate the expenses associated with each investment option and consider how they align with your investment strategy and goals.
In summary, the cost and fees of mutual funds and ETFs differ, with mutual funds typically having higher management fees and ETFs having lower fees. Understanding these costs and fees is essential for making informed investment decisions.
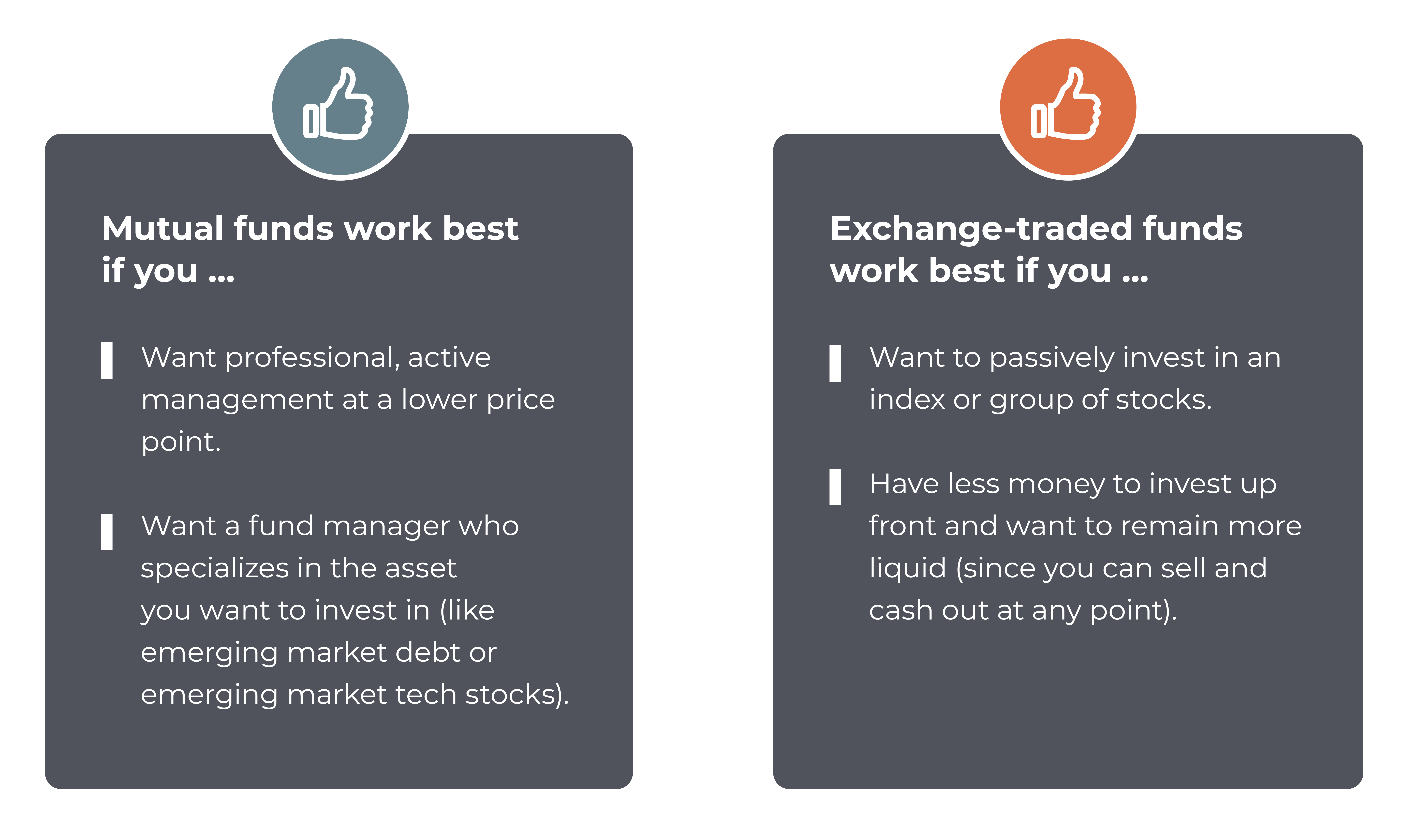
Conclusion: Choosing Between Mutual Funds and ETFs
Factors to Consider When Choosing
When deciding between mutual funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs), it is important to consider a few key factors. First and foremost, you need to evaluate your investment goals and risk tolerance. Mutual funds are typically better suited for long-term investors who prefer professional management and are willing to pay higher fees. On the other hand, ETFs are more suitable for investors who want flexibility, lower costs, and the ability to trade throughout the day.
Another factor to consider is the investment strategy. Mutual funds are actively managed, meaning that the portfolio managers make decisions on what securities to buy and sell. ETFs, on the other hand, are passively managed and aim to mirror a specific market index. If you prefer a hands-off approach and believe in the efficiency of the market, ETFs may be a good fit for you.
Which is Right for You: Mutual Funds or ETFs?
The decision between mutual funds and ETFs ultimately depends on your individual needs and preferences. If you value professional management, are comfortable with potentially higher fees, and plan to hold your investments for the long term, mutual funds may be a wise choice. On the other hand, if you prefer flexibility, lower costs, and the ability to trade throughout the day, ETFs could be a better fit.
It's important to assess your investment goals, risk tolerance, and the specific characteristics of each investment vehicle before making a decision.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Both mutual funds and ETFs offer unique advantages and disadvantages. It's crucial to thoroughly research and evaluate your options before making a decision. Consider consulting with a financial advisor who can provide personalized guidance based on your specific financial situation.
Remember, investing involves risk, and past performance is not indicative of future results. Regularly review your investments, reassess your goals, and make adjustments as needed to stay on track towards achieving your financial objectives.



